Introduction to Autodesk Revit
Revit, by AEC software powerhouse Autodesk, is a BIM software, perhaps one of the most popular of its kind in the AEC industry. Architects, engineers, and other building professionals use Autodesk Revit at almost every project stage to design, coordinate, and document building information in a single environment.
Its BIM-based workflows help teams work on the same model, reduce errors, and support smarter decisions during design and construction.
In this guide, we’ll cover the key tools, features, and learning steps every beginner should know to confidently start using Revit in 2026. Revit is one of the most powerful BIM tools used by architects and engineers. This beginner’s guide explains Revit’s features, tools, and workflows while helping you learn how to use it confidently.
1. When, how and why did it emerge?
Revit software originally was not a part of Autodesk which was later acquired in 2002. It was first developed as part of Revit Technology Corporation in 2000 to bring parametric modelling into the industry. After the purchase, Autodesk further researched and developed the software into the Revit we know today. From then on, 3D modelling in Revit allows embedding both geometric and non-geometric information in the model.
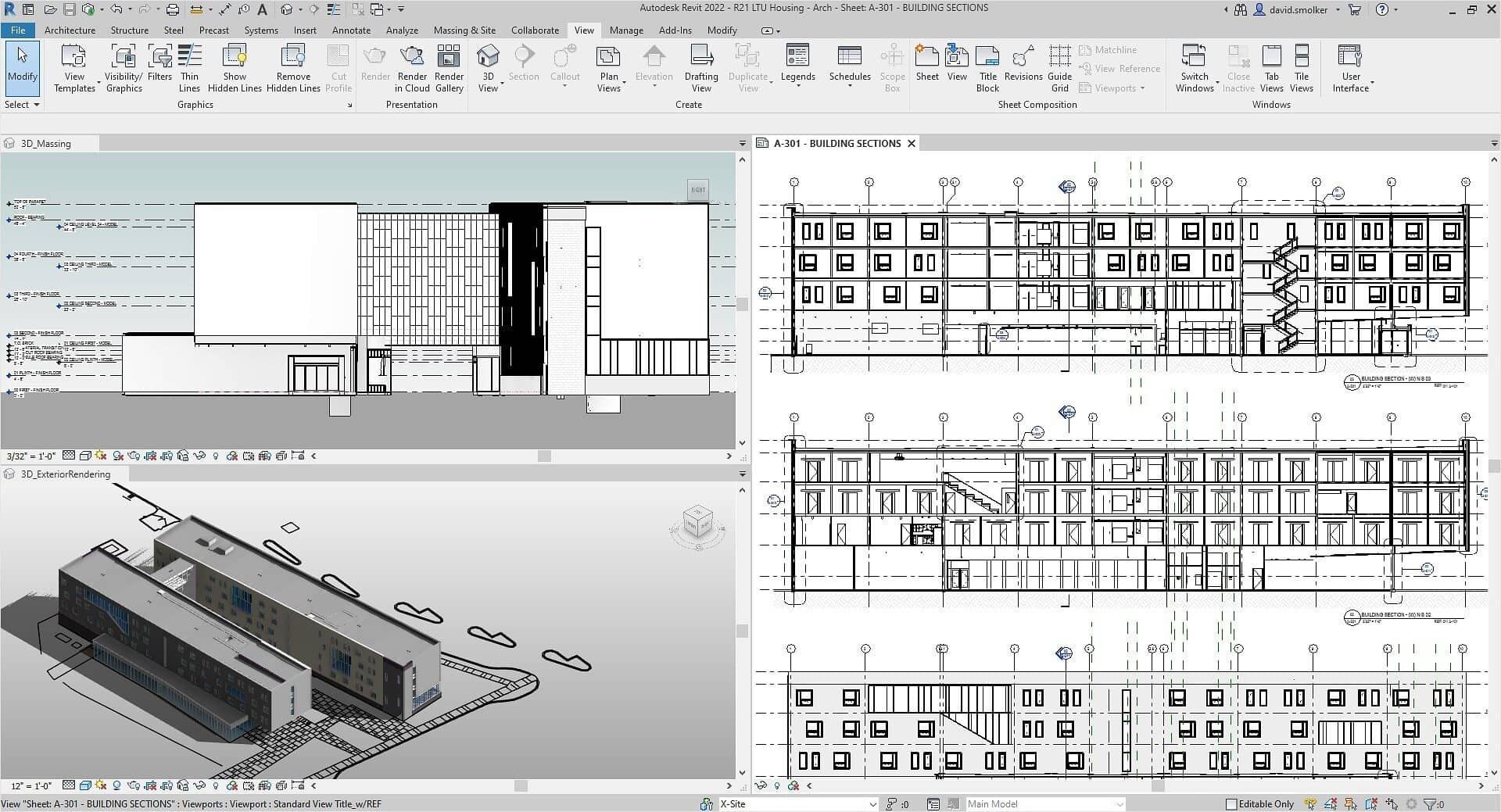
2. Software overview

With Revit, both parametric and direct (or non-parametric) modelling are possible, giving architects the ability to create unlimited design iterations while establishing efficient design and construction workflows in BIM.
3. Revit as the prime BIM software today
Autodesk Revit has gone through several iterations and upgrades over the decade to be more inclusive with different disciplines in the industry. All the concerted efforts have paid off as it is now the prime BIM software in the industry used by architects, engineers and contractors. The functions of Revit offer productivity from the very first stage of the design until the operations after construction.
4. Revit vs BIM
It is a common misconception that Revit is BIM and vice versa. Let us reiterate again that this is absolutely wrong! BIM is a methodology that covers many AEC industrial workflows including designing and documenting. And Revit is one of the software that allows such workflows to happen. In simple terms, Revit is one of the BIM software.
5. Revit vs CAD
To explain the relation between the two, you should first understand the difference between BIM and CAD. BIM stands for Building information modelling - you create building models with information embedded in them. Meanwhile, CAD stands for Computer-Aided Design which allows you to create 2D and 3D drawings and models. Revit, as a BIM software, allows creating models that are beyond 3D and have valuable data attributes crucial to a project workflow.
Also Read: Architecture Thesis Topics: A Comprehensive List of 30 Topics to Pick From
Key Features of Revit
1. BIM Modelling
Best known for BIM, Revit streamlines workflows to create BIM models that are rich in data in a singular and centralised file. It allows all project stakeholders to contribute and make informed decisions. As the model is created with BIM methodology, any modification to it will get reflected in all related parts, components and views. Whether it is parametric or non-parametric, they will still be BIM models regardless.
2. Designing & Collaborating
It is unacceptable to not include collaboration when we are talking about BIM. No matter what software we use, BIM models contain data meant to be shared and collaborated on. All project information would be established in a single database so that every team member can access and modify their respective data easily. Tools such as BIM 360 are a must-have for collaboration work in Revit.
3. Beyond Modelling & Collaboration
Throughout the modelling stages, the 3D model may go through analyses to ensure the design is energy-efficient and responsive to user and site conditions. With sustainability in mind, architects can now effectively analyse sustainable elements using Revit, including energy efficiency and heat gain, while also performing facade studies. All the sustainability analysis information can be uploaded to the BIM model to be shared with the project team.
Once the 3D model is complete and the project moves to the next stages, the model will continue to be developed in terms of its embedded data. Not only architects but also contractors and engineers can manage and supervise the project stages both on and off-site, determine cost estimates and scheduling based on this data. We call such classification BIM Dimensions.
Revit for Different Industries
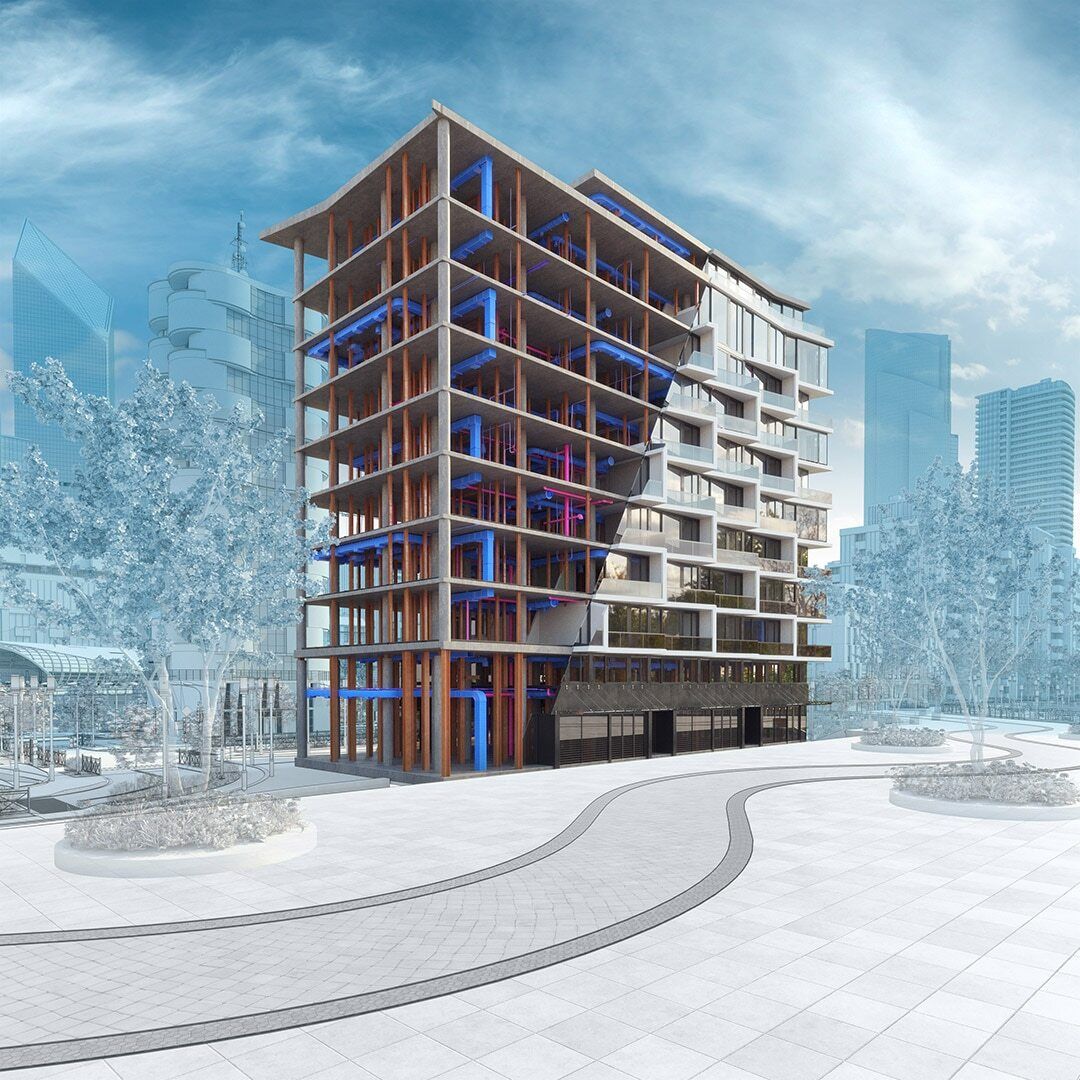

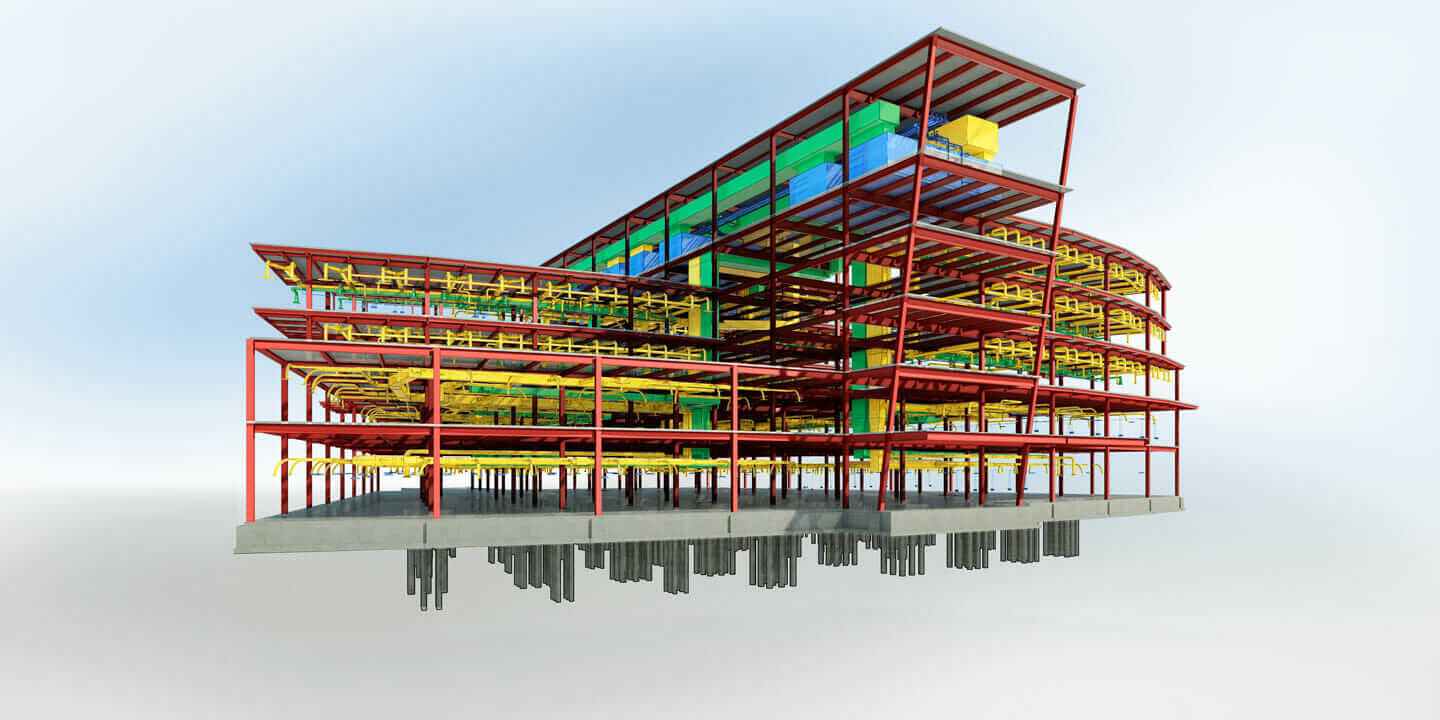
Partial model in Revit
We can classify Autodesk Revit’s features by different industries - mainly Architecture, MEP (Mechanical, Electrical & Plumbing), Structural and Construction. Despite this classification, all these features come under one software, allowing every professional to work in the same file formats. All AEC professionals, no matter the industry, can utilise this software to produce high-performance buildings and infrastructure.
1. Revit Architecture
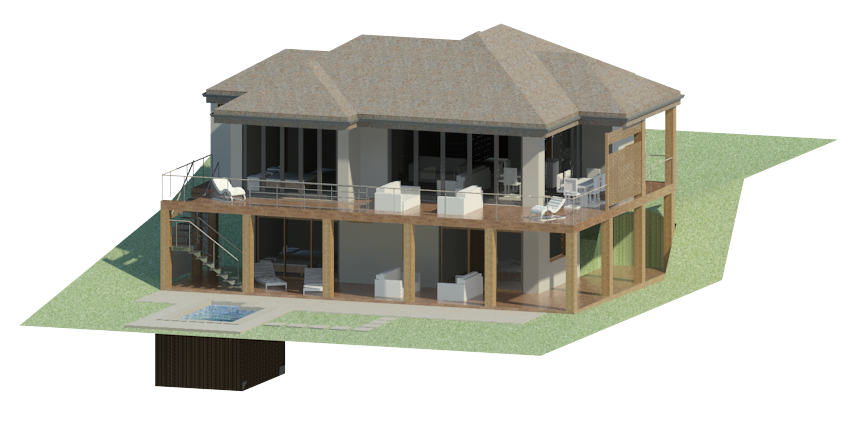
Modelling in Revit is made easy with its vast content libraries and its function to place walls, windows and doors with accuracy. 2D drawings – plans, sections and elevations – can also be generated quickly. What makes it even better? They are accurate, unlike the CAD drawings from Sketchup, as they are generated live from the drawing. Revit Architecture also permits architects to analyse building performance and energy efficiency during the early design stages for an optimised design. Once the design has been finalised and needs to be presented to the client, the software can create photorealistic renderings of the model.
2. Revit Structure
Structural engineers can use Revit to detail reinforcement designs and produce shop drawings. As engineers need to focus more on the details, Revit supports these requirements by design-to-detail workflows. Due to this, Steel design, detailing and structural analyses necessary in infrastructure projects can easily be provided by the structural engineers.
3. Revit MEP
Revit MEP was developed to bring MEP engineers into the fold for a complete package for the AEC industry. The functions of architectural modelling in Revit was considered inadequate for MEP engineering and so Revit MEP especially targets electrical, mechanical and plumbing engineering functions together with additional content libraries.
What Professionals is Revit Ideal for?
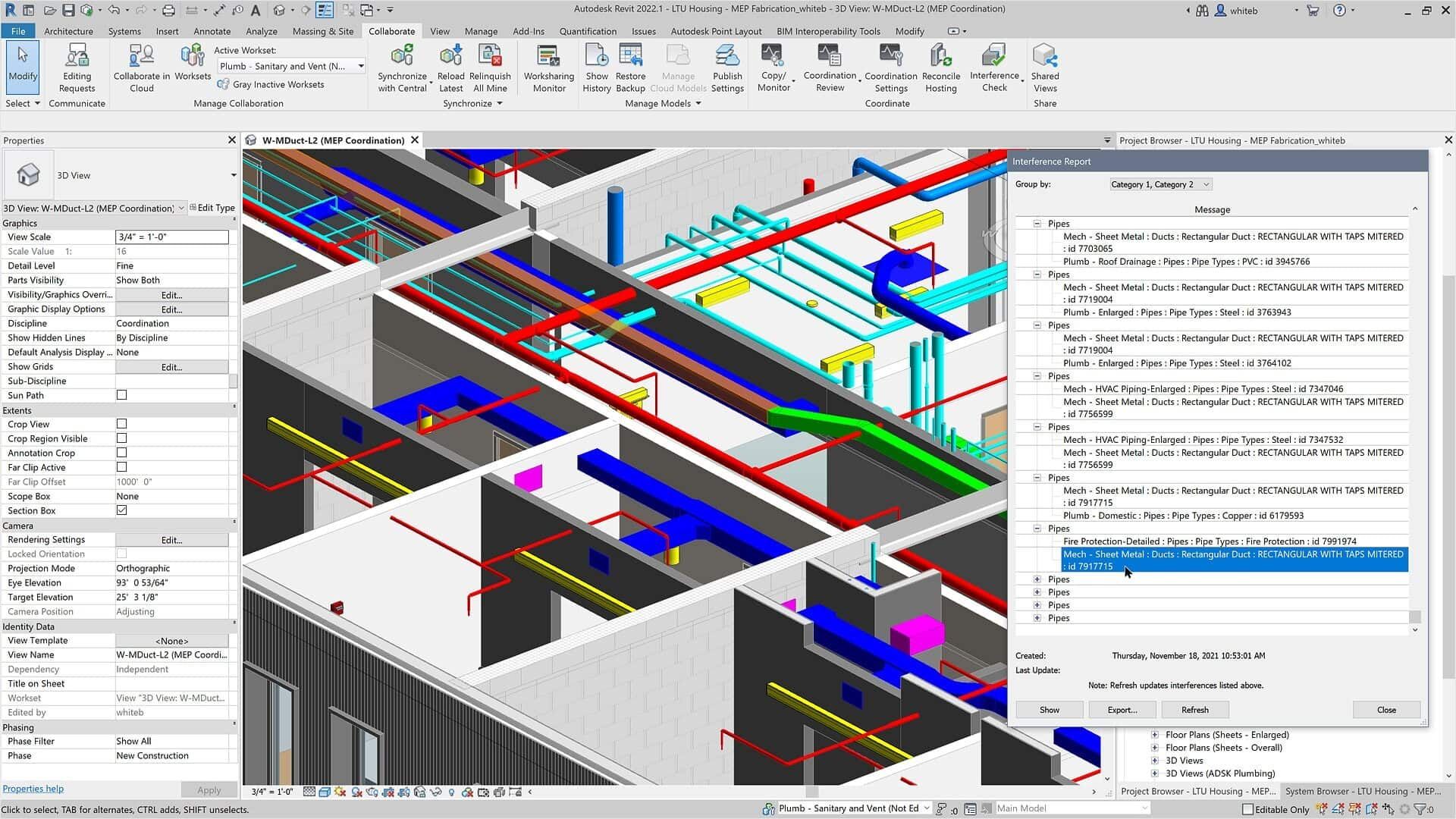
The efficient interoperability and collaboration provided by Revit assist all AEC professionals with their workflows. For architecture and design professionals –architects, landscape architects and interior designers etc, Revit provides assurance that the later processes can also be handled in the same software. Cost & schedule estimates, prefabrication and visualisations are some benefits Revit can provide for these professionals.
1. Engineering Professionals
Engineering professionals and project managers nowadays use Revit as one of the main BIM software to design and oversee projects. The nature of their responsibilities, however, means that other software (e.g. Navisworks) might be necessary at some stages. Regardless, Revit offers enough flexibility and capacities to model and document BIM projects (MEP, structural and Civil) of all sizes
2. Architects
Nowadays, when you look at a job posting for an architect or a BIM professional, you will not miss Revit as a skill requirement for the job. It has become one of the most in-demand software thanks to its BIM capabilities. Revit offers smooth collaboration between the architect and other stakeholders with its numerous plugins and add-ons, further augmenting the process. By knowing just this tool, architects can conceptualise, finalise, visualise and document design and any related processes till the final product.
Ease of Modelling & Learning in Revit
1. How easy or tough is it to learn Revit?
Revit, frankly, is not one of the easy software to learn for beginners. Its interface with many ribbons and their functions makes it less intuitive than other modelling software like Sketchup. However, bearing in mind that these tools make the project workflows more efficient, they allow multidisciplinary coordination for streamlined project delivery.
2. Ease of Modelling, Drafting and Navigation in Revit
When using Revit, one can just focus on creating the 3D model as the 2D drawings are just extracted from it. However, it is a bidirectional relationship; any change in the 2D view can also affect the 3D model. For direct modelling, the process is quite straightforward. On the other hand, for parametric modelling, Revit requires plugins such as Dynamo and Rhino.Inside.Revit.
Many new users find modelling in Revit formidable. Not only are there many functions to comprehend, but one might also need to familiarise with so many buttons. However, it will give a high return on investment value since Revit can efficiently aid in BIM workflows.
Practical Ways to Get Started with Revit Learning
If you want to master Revit as a beginner, it helps to follow clear Revit learning paths instead of exploring tools at random. Focusing on small steps will make it easier to learn Revit basics and build confidence with real projects over time.
-
Start with the official Autodesk Revit tutorials to understand the interface, basic commands, and common BIM workflows.
-
Follow a structured Revit software training course that covers modeling, views, sheets, and basic documentation for Revit for beginners.
-
Practice on simple sample projects like a small house, room layout, or interior design to apply tools in a realistic context.
-
Join online communities and forums where learners and professionals discuss Revit 2026 features, tips, and troubleshooting.
-
Set a regular practice schedule so you keep learning Revit step by step instead of trying to master everything at once.
With practical practice, guided lessons, and small real-world exercises, beginners can move from just watching tutorials to actually using Revit with confidence on AEC projects.
How does Revit compare with other popular BIM Software?
1. Revit vs ArchiCAD
ArchiCAD is known as the first BIM commercial software. It has gone through upgrades and its current functionalities are similar to Revit’s.In fact, it is more popular in some regions than Revit because of its light operating system requirements for streamlined BIM workflows. ArchiCAD creates BIM models that can be used to generate 2D CAD drawings while supporting many file formats – including .dwg and .skp files. From sketches to detailed drawings, ArchiCAD provides features for all design stages.
2. Revit vs Vectorworks
Vectorworks is similar to Revit wherein architects can use the software for 2D, 3D modelling and BIM. Released by another name from Nemetschek, it comes in the form of four main products – Architect, Landmark, Spotlight and Fundamental – which architects and designers can choose based on their needs. Vectorworks software is made for maximum creativity and many consider it to be more intuitive and easier to use for modelling than Revit. Users can synchronize and collaborate on their works through cloud services; at the same time, Vectorworks also support openBIM and IFC (Industry Foundation Classes) formats. Vectorworks is more suitable for architects and designers as it offers intuitive and flexible tools for 3D modelling.
Also Read: Top 7 Places to Learn BIM (Building Information Modelling) in India
Plugins for Revit
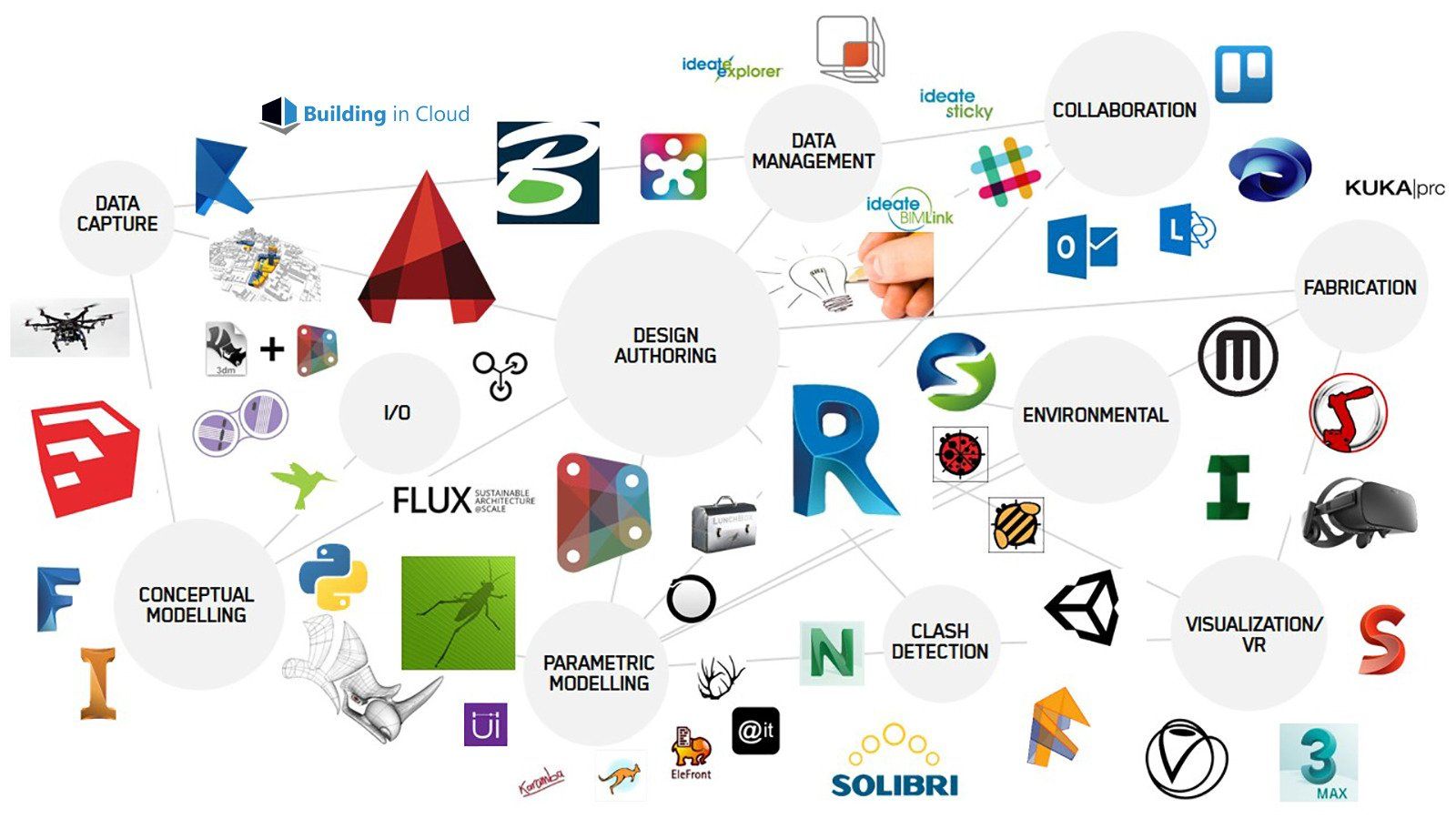
The functionality of Revit software is further complemented by various plugins and add-ins for all workflows. These plugins can be either from Autodesk itself or from third-party developers. The list of plugins for Revit is endless. Do you need a tool for parametric modelling? There are Dynamo and Rhino.Inside.Revit. Do you want to render your BIM models? Enscape and Twinmotion are popular options.
1. Dynamo
Dynamo is undoubtedly one of the most well-known plugins of Revit. Like how Grasshopper goes together with Rhino, Revit with Dynamo allows computational design creation and automation in its interface without needing another software.
2.pyRevit
Then there is pyRevit to solve the troublesome issues of Revit and enhance your workflow, a plugin that comprises several tools. Many users of this tool find it helpful to work on tasks that would otherwise be inefficient in Revit’s interface.
3. Rhino.Inside.Revit
Thanks to the availability of Rhino.Inside.Revit plugin, we can now document parametric models for BIM workflows in Autodesk Revit. This plugin delivers the essential integration of Rhino 3D’s interface into Revit’s, along with Grasshopper as part of Rhino 3D. Architects can produce native models with Revit components and Grasshopper scripts for a streamlined workflow of parametric design and BIM. Grasshopper can also run on its own in Revit’s interface, without needing to have Rhino 3D as an intermediator.
There are just three of the most popular plugins for Revit. To find more plugins, you can visit our Popular Revit Plugins for Effective BIM workflows page.
Our Revit plugins list barely scraped the surface of the large number of plugins available, just from Autodesk alone. Combine it with the tools from third-party developers, you will never run out of plugins to choose!
Rendering with Revit
1. Rendering Tool Plugins
Revit’s capabilities are not limited to only modelling and documentation with BIM. Architects need to produce rendered images of the model to present to the client. Rendering or visualisation software can generate photorealistic images, thereby letting the client understand how the end product will look.
For creating drawings and renderings, Revit works, as well as any other modelling software if not better. And most visualisation software have integration with Revit. Each with its own benefits, visualisation tools for Revit include Enscape, Twinmotion and Lumion and more.
2. Native Rendering in Revit
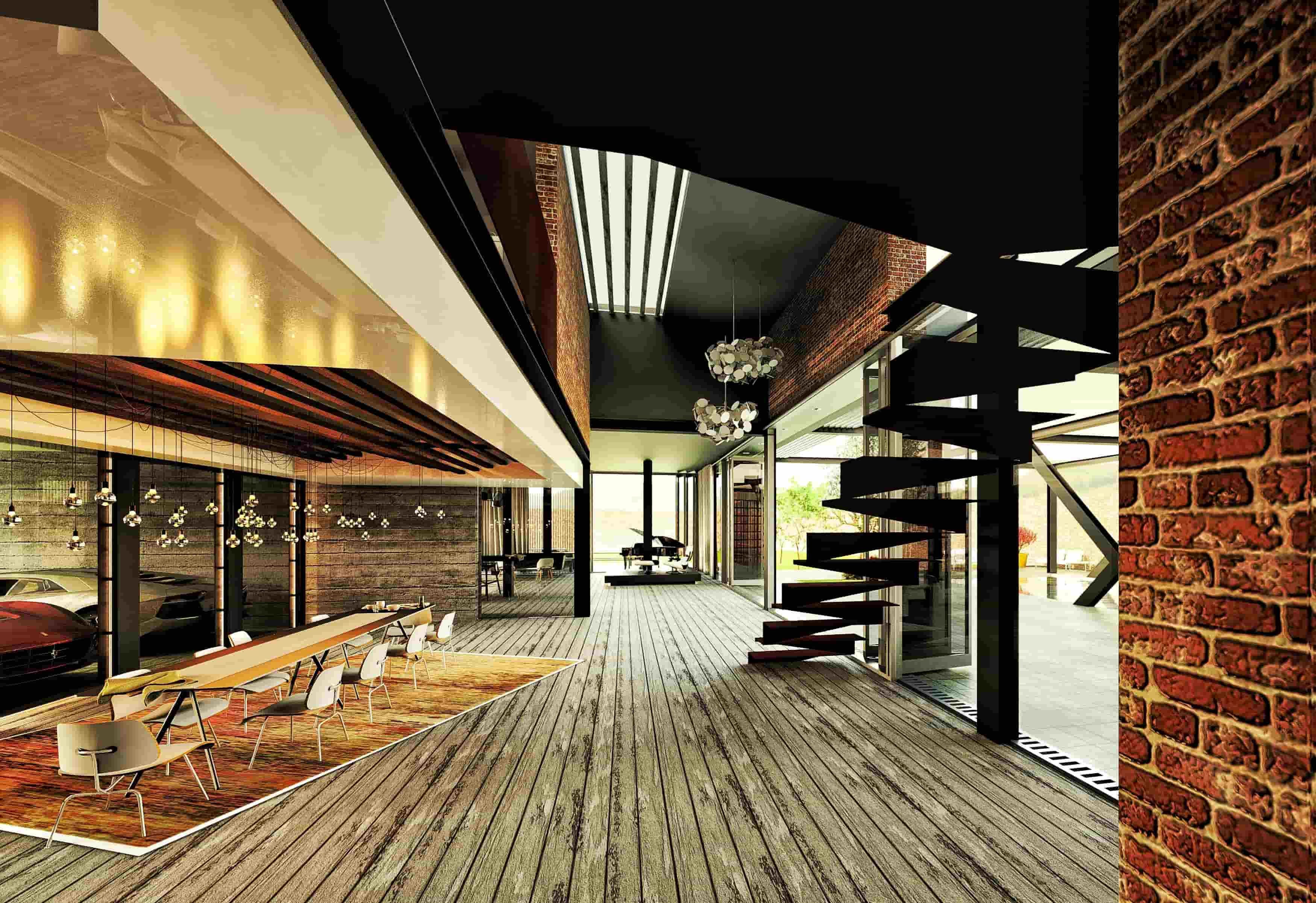

In addition to these applications, Revit also comes with its own rendering engine, albeit less powerful than the software. Despite the lack of its popularity, Autodesk Raytracer can still deliver high-quality renders in Revit. The other option is the Autodesk Cloud rendering which offers not only high-quality rendering but also batch rendering, solar study renderings and interactive panoramas.
Downloading Revit and Cost of Licences
Like most Autodesk products, Revit’s licences are subscription-based. They come in 3 options - $365 monthly, $2910 annually or $8730 for three years. Students and educators can rejoice; Autodesk provides free and renewable educational access to the software.
Revit can be easily found and downloaded on the Autodesk website. Just make sure to check for the latest version and the system requirements for it before you install it.
How can you learn Revit?

It is a known fact that Revit is not an easy software to learn. As Revit has such a vast range of functions, learning it on your own can be quite a challenge. Consider taking a course to master the software. Some BIM courses and certifications, such as Autodesk Revit software certifications, are recognised by major AEC firms as a testament to your skills.
However, in most cases, employers are looking for professionals skilled in different aspects of BIM, meaning knowing Revit is not enough. Hence, one should learn to use Revit as a means to aid BIM workflows.
Conclusion
Revit is an extremely powerful software that helps architects, designers and engineers alike. Its functionality among a vast range of tasks and stakeholders, makes it one of the ideal BIM software tools.
It eases the work by creating a seamless flow through diverse teams. If you are looking to learn this tool and dive deeper into the world of BIM, Novatr's can help you with it.
Novatr’s BIM Professional Course helps learners to:
● Master BIM workflows using Revit and related software
● Familiarise themselves with useful Revit plugins and tools
● Study part-time with both live and recorded sessions for continuous learning
● Explore industry-relevant BIM methodologies and work on RIBA-structured project
● Learn from BIM experts from top AEC firms worldwide
● Begin a career in BIM industry with placement assistance
Start mastering Revit with hands-on practice and structured learning paths. Explore the BIM Professional Course for Architects offered by Novatr to gain the practical skills needed for real-world AEC projects. You can also go to our Resources page to learn more about BIM.
FAQs
1. Is Revit easy for beginners to learn?
Revit can feel challenging at first because of its many tools and ribbons, but beginners can learn it step by step with simple projects, guided tutorials, and structured Revit software training.
2. How long does it take to learn Revit?
Most beginners can grasp basic Revit workflows in a few weeks of regular practice. Reaching a professional level usually takes a few months of focused learning and working on real or sample projects.
3. What are the best ways to start learning Revit?
The best way to start is to follow beginner-friendly Revit tutorials, take a structured course, and practice on small models like rooms or houses. Combining videos, exercises, and feedback speeds up your learning.
4. Which Revit version should beginners use in 2026?
Beginners should use the latest stable version of Revit available in 2026, since it includes updated features, bug fixes, and better support for current BIM workflows and plugins.
5. Is Revit better than AutoCAD for architectural design?
For architectural design and BIM workflows, Revit is usually better than AutoCAD because it creates smart 3D models with data, not just 2D lines. AutoCAD is still useful for drafting, but Revit is more powerful for BIM-based projects.
Was this content helpful to you











