Hailed as a paragon of design technology, parametric modelling is soaring in popularity for its endless possibilities for modelling and design creation. So, naturally more and more architects and designers have started using it. Then let’s see what are the best parametric modelling software!
But first, what exactly is parametric modelling?
What is parametric modelling?
It is essentially a method of computational design that can create 3D models based on algorithms or parameters. The design is achieved by tweaking the ‘parameters’, the attributes to the model’s geometry, with the aid of algorithmic capabilities; in essence, it minimises design homogeneity and enables free-form modelling.
Why should architects use parametric design software?
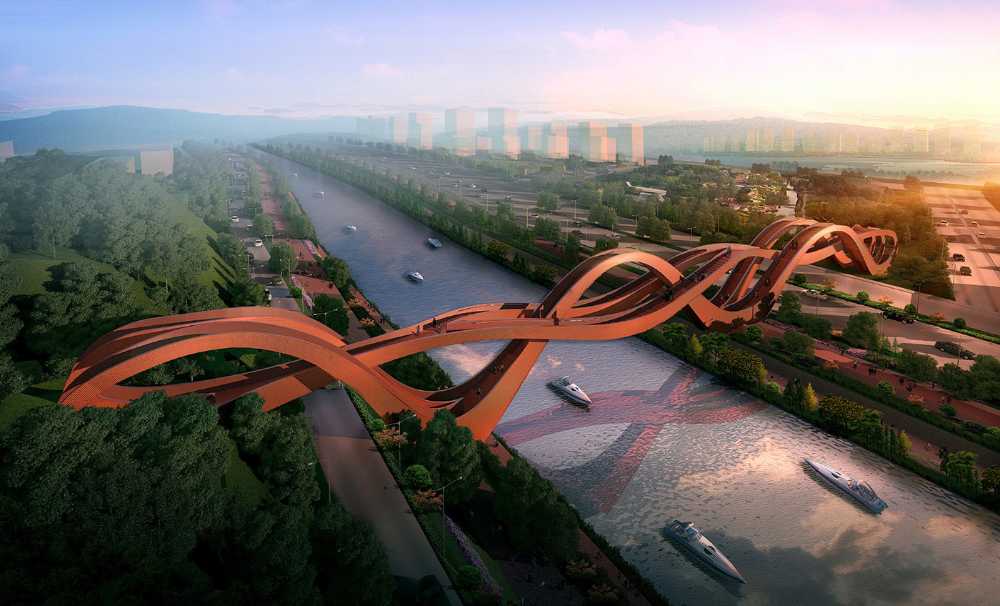
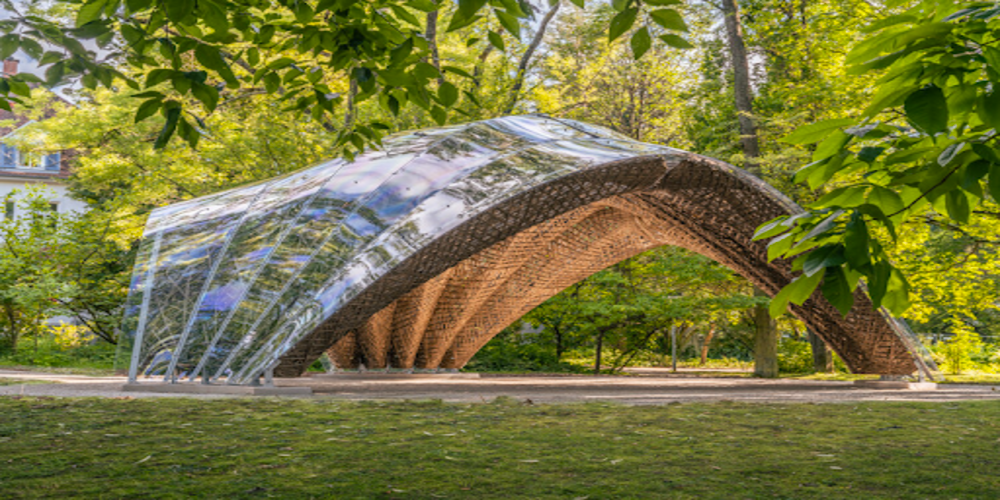
Thanks to parametric modelling, architects can design more organic and complex buildings, both in forms and design inspirations. Nature is where we can observe systematic amalgams of design concepts and parametric capabilities enable such ideas to give each building character instead of just ‘boxes’. Additionally, by exploring and testing different materials for construction, such as bamboo, the concept of a concrete jungle may finally disappear.
Just because it is heavily associated with forms it does not mean that is the limit. Even in interior design, the power of parametric modelling offers various architectural solutions for a more effective design.
Why should designers use parametric design software?
The parametric capabilities greatly influence not only the design but also the workflow. A change to a parameter can generate many new design iterations according to the rules and features of the software. What’s more, any revision gets updated on associated parts, assemblies as well as views, hence fewer broken links and less tedious manual updates. During the modelling process, the designer can identify spatial interference, and afterwards, perform fluid flow, thermal performance analysis and manufacturability checks. Creating a parametric model may take longer initially but this investment returns ten-fold later on, saving both cost and time.
The Top 6 Parametric Modelling Software
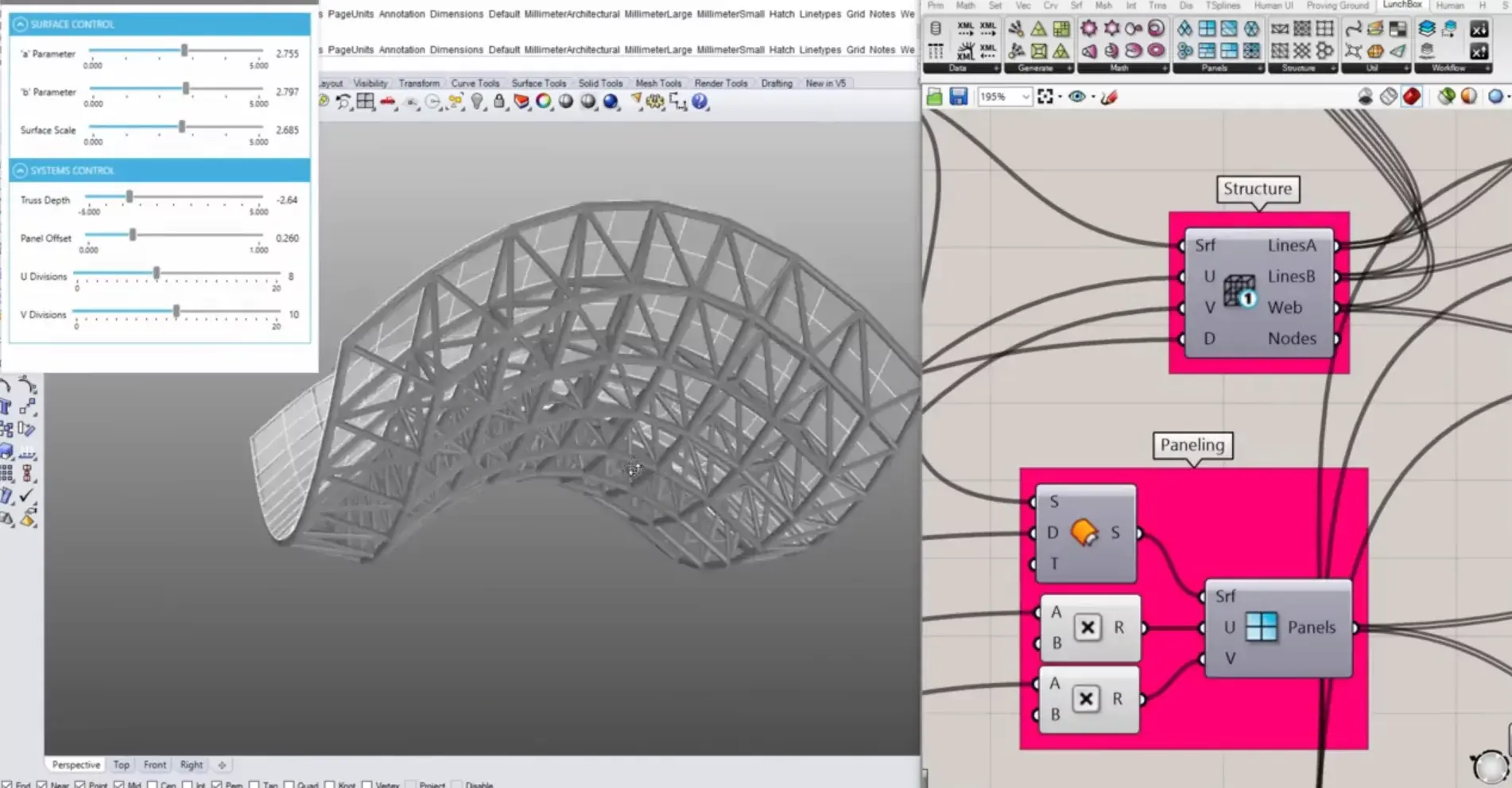
1. Rhino with Grasshopper

Most, if not all, architects and designers know Rhino even if they are not familiar with it. And if you know Rhino, you will, and should, also know Grasshopper. Together, they are the front runners for parametric modelling, loved by both architects and designers alike. Both have the same developer, Robert McNeel & Associates, with Grasshopper released years later to extend Rhino 3D’s modelling abilities to parametricism, removing any limits to designing highly complex forms.
Key Functions and Use:
Rhino works on NURBS (Non-uniform rational B-spline) and is used extensively in various fields, including architecture, engineering and jewellery design. Despite Grasshopper being a visual programming language that runs with Rhino, one does not need to know any programming language to use it. It works virtually by manipulating ‘nodes’ to create a sequence for the final output.
In addition, Rhino together with Grasshopper, and the many plugins that come with it, can also be used for performance and structural analyses and fabrication etc. Hence, it can be used by a wide range of professionals. Despite the common misconception, Rhino and Grasshopper are not difficult to learn at all. Here's your guide to know how easy it is to learn Rhino and Grasshopper.
Cost:
The pricing for the full package of Rhino 7 for a single user is $195 for students and $995 for commercial use. There is no separate installation required as Grasshopper is already integrated with the latest versions of Rhino, Rhino 6 and 7.
2. Solidworks

Owned by Dassault Systèmes, Solidworks is parametric modelling software that is more popular with engineers as it can easily create electrical, mechanical and automotive components.
Key Functions and Use:
It comes with numerous tools for planning, fabrication, simulations and validation. In addition to parametric modelling, it also combines CADD (Computer-aided design and drafting), CAM (Computer-aided manufacturing) and CAE (Computer-aided engineering) systems.
Modelling is not all it can do; that model can be used to estimate cost and manufacturability checks. Its abilities can rival that of Rhino’s and is equally popular in some parts of the world. With Solidworks, any advanced designs, from product to mechanical to parametric architecture, can be efficiently planned and created.
Cost:
Solidworks’s student edition costs $99 per year, with an additional $60 for 3DEXPERIENCE Solidworks. There is different pricing for commercial, academic and research uses.
3. CATIA

CATIA, also by Dassault Systèmes, is widely used for product design, as parametric modelling software and also PLM (Product Lifecycle Management) software. Its strength dominates the automotive and aeronautics industries.
Key Functions and Use:
However, that does not mean that it cannot be used by construction professionals. Its latest version, CATIA 3DExperience R2022X, combines shape sculpting modelling (control-points manipulation) with parametric associativity. This enables designers to explore more design ideas and make relevant changes efficiently. CATIA can also create and animate virtual human models for better simulation and validation of the product according to user requirements and experience. This is an advantage, especially in the automotive industry where human avatars are needed for ergonomics and safety checks.
Just modelling is not the end; it takes it a step further to allow users to venture into virtual reality. The Collaborate Designer feature also enables creating and visualising linear infrastructures, electrical, piping and mechanical components.
Cost:
The pricing for a student package is $60 (60€) excluding tax, and for Academics, the price starts at 30€ per student for a classroom.
4. Fusion 360

Fusion 360 is an Autodesk cloud-based 3D modelling software that integrates CAD, CAM and PCB (Printed circuit board) features for product design and manufacturing.
Key Functions and Use:
As a 3D modelling software, it comprehensively includes both parametric and non-parametric, or direct, mesh and surface modelling tools. Therefore the user can choose what to work on based on the need and the skill of the user. As it is also cloud-based, Fusion 360 allows a design team to centralise all activities and communicate effectively in real-time. The software also includes electronics and PCB design tools for powerful product modelling.
The 3D models can also be documented into 2D drawings with annotations. Moreover, not only are local and cloud rendering available, but also animations and exploded views can be created for better presentation. With the Simulation Extension (a paid subscription), manufacturability and performance under real-life conditions can be accessed through a set of simulation study types.
Cost:
Pricing for Autodesk products is subscription-based. The subscription for Fusion 360 software alone costs $60 per month ($372/year on discount currently) and the extensions’ from $372 annually.
5. Inventor

The next Autodesk software on our list is Inventor, parametric modelling and CAD software mainly for mechanical designs. Similar to Fusion 360, it has an intuitive user interface and is capable of direct, free-form and rules-based design, in addition to parametric modelling.
Key Functions and Use:
Inventor tests the combination of the design by accessing the fit and function and identifying interference patterns before rendering, documentation and planning for manufacturing processes can begin. Components can be easily placed and assembled with a list of commands available. It also supports inserting third party design components and models directly into the assembly.
This is not enough, and clients are asking about BIM? No need to worry! The 3D model in Inventor can be converted to BIM objects with BIM exchange tools. This means the architect or the designer can now participate in BIM projects. Revit models can also be inserted into the Inventor 3D model for further modifications.
Cost:
The subscription for Autodesk Inventor starts at about $290 per month or $2300 annually. There’s also the option to subscribe to Product design and Manufacturing Collection at $375 per month.
6. Creo Parametric

This is a 3D CAD solution software, with a parametric modelling iteration by PTC Inc. (previously known as Parametric Technology Corporation), a leading tech company that provides digital solutions to engineering, manufacturing and industrial services.
Key Functions and Use:
The 3D design in Creo is aided by parametric and freestyle surfacing features as well as CAM and Generative design. These features allow curves and surface manipulation by transforming, scaling, stretching, tapering the geometry etc. The 3D parts and their assembly are created with precise geometry, regardless of the complexity, for efficiency, time and cost-effectiveness. These models can then be accessed for both static and dynamic interference detection.
As Creo Parametric is heavily focused on mechanical and product design, its design capabilities also aid in such design projects. For example, with Intelligent Fastener Design, any holes and assembly fasteners can be automated while utilising the integrated web-based component catalogue. Sheet metal design, piping and cabling designs are all feasible with Creo with its modelling and analysis capabilities.
Cost:
Creo releases are in packages with different features and prices. The Creo Design packages start at $2550 for a licence.
Given its popularity, Parametric modelling is predicted to be the new norm in the future. Be a part of the forward-thinking and learn this new craze with Novatr’s Parametric Modelling Certification Course taught by industry experts. To read more about parametric design and software, go to our Resources page!
Was this content helpful to you