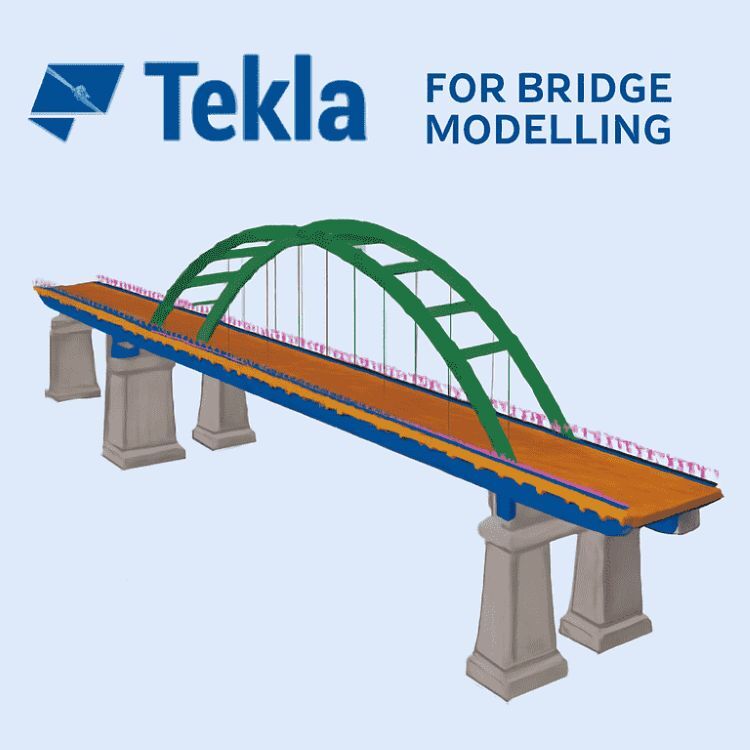
Bridge modelling forms the essential aspect of civil engineering that involves accuracy, effectiveness, and sophisticated software programming tools. The powerful bridge modelling software known as Tekla Structures has become very popular in modelling bridges due to the ease with which it handles complex buildings. It is known that Tekla Structures is currently the most effective Bridge Information Modeling (BIM) software in the market, particularly in double-curved bridges and complex designs.
This blog analyzes how bridges can be modeled in Tekla, including some of the most relevant processes and features that exemplify why Tekla is one of the preferred bridge modeling systems for bridge engineers.
Why Choose Tekla Structures for Bridge Modelling?

Tekla Structures offers a range of capabilities that make it ideal for modeling bridges with Tekla Structures:
1. Parametric Modeling
Tekla enables engineers to build parametric models, and this means every time a design change is included, the model automatically changes, ensuring a high degree of flexibility and accuracy.
2. Rebar Detailing
Tekla is also important regarding detailed reinforcement versus final design detailing. We must see that we have met industry standards and maintain structural integrity.
3. Fabrication Ready Outputs
The resultant gives one fabrication-ready output, and the construction process develops directly out of the design with accuracy and precision.
4. Tekla Concrete & Steel Modeling
Tekla supports both Tekla concrete modeling and Tekla steel modeling, giving engineers the flexibility to work with various materials and structural types seamlessly.
If you need to convert IFC to a Tekla model, Tekla provides tools for seamless integration. These tools allow for the easy conversion of Industry Foundation Classes (IFC) files to the Tekla native format.
Understanding Tekla Environment for Civil Engineers

Before diving into bridge modelling, it’s important to understand the Tekla environment and how it can help civil engineers:
- 3D Modeling: By creating Tekla 3D modeling of bridge structures, the Tekla software offers an intuitive interface to build a highly accurate 3D model of the whole bridge with views of every component.
- BIM Integration: Tekla works well with other BIM tools in that it flows data across disciplines.
- Collaboration: Tekla is the collaborative aspect, since various engineers can perform various tasks on the same project simultaneously, reducing time and improving the level of coordination.
- Reinforcement Detailing: Automated reinforcement detailing ensures that no design requirement is overlooked in detailing, such as in concrete buildings.
Modeling Bridge Superstructures (Girders, Slabs)

To model a bridge superstructure in Tekla, including girders and slabs, follow these steps:
- Step 1: Start with the Bridge Alignment: Define the path of the bridge using Tekla’s alignment tools, ensuring it fits the geographical layout.
- Step 2: Create Parametric Profiles: Use Tekla’s parametric profiles for beams and slabs. These profiles automatically adjust to the design parameters.
- Step 3: Place Superstructure Components: Locate the girders and the slabs according to the bridge layout.
- Step 4: Define Structural Connections: It defines structural connections between structural elements, which the designer should design.
- Step 5: Finalize Geometry: After all the parts are placed, the structure's geometry, including the required curves or angles to make the bridge, is automatically developed in Tekla.
Substructure Modeling

Substructure modeling is crucial in ensuring the bridge’s stability and integrity. In Tekla, this includes the following:
- Piers: Design model piers according to bridge span and support needs with the Tekla 3D modelling capabilities of the Tekla product..
- Footings: Define reinforced concrete footings, giving their exact dimensions and reinforcement.
- Abutments: Model abutments and ensure they are connected to the surrounding terrain or foundations.
Adding Rebar and Construction Phasing
Incorporating rebars and designing stages of the construction are important components of the modelling procedure of the bridge in Tekla:
- Rebar Detailing: Have reinforcement detailing tools in Tekla. The tools give the accuracy required to model concrete inside Tekla and ensure the layout of such reinforcement is according to the design.
- Construction Sequencing: Tekla enables you to specify construction phases and present them visually, ensuring that the bridge will be assembled in the proper sequence and all the activities will be properly scheduled.
How to generate drawings, Reports, & Clash Detection
Once the model is complete, Tekla makes it easy to generate drawings, reports, and perform clash detection:
1. Export Drawings:
You can easily export drawings from one Tekla model to another, ensuring consistency and reducing the chance of errors. Tekla automatically generates construction drawings based on the 3D model, and the process of how to export drawings from one Tekla model to another ensures that all details and references are transferred seamlessly.
2. Reports:
Tekla produces comprehensive reports, including material takeoffs, reinforcement schedules, and quantity lists, which are essential for project management and budgeting.
3. Clash Detection:
Tekla’s clash detection tools allow you to identify any conflicts in the model before construction, reducing costly errors and rework.
Real-Life Usage of Tekla for Bridge Modelling in Infrastructure (US / UAE Projects)
Tekla has been successfully used in large infrastructure projects worldwide, with significant contributions in both the UAE and the US.
USA:
In the United States, Tekla has been a go-to tool for numerous highway bridge projects, such as the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge (East Span) and the I-10 Overpass Bridge. Its ability to handle complex geometries and integrate seamlessly with BIM processes has made it essential for civil engineers, ensuring accuracy and efficiency in bridge design and construction.
UAE:
Tekla played a key role in designing and modeling high-profile bridge projects, including the Sheikh Zayed Bridge and Al Garhoud Bridge. Its precision in detailing and reinforcement design was crucial to the success of these iconic structures.
Tekla Modeler Salary:
The Tekla modeler salary in India and other regions depends on experience and skills.
- India: Salary for a Tekla modeler in India ranges from ₹25,000 to ₹40,000 per month.
- USA: In the USA, Tekla modelers earn between $57,000 and $100,000 annually, depending on experience.
- UAE: In the UAE, salaries for Tekla modelers range from AED 3,000 to AED 6,000 per month.
Master Tekla Along With BIM
A person should learn Tekla and BIM. Tekla integrates well with BIM and is a very useful tool among bridge engineers. Perfecting both skills will be an effective way of improving your career.
Our Building Information Modelling (BIM) Course for Civil Engineers equips you with industry-relevant Tekla workflows using live projects, which are an essential component for those engineers seeking jobs in infrastructural firms or design-build consulting firms.
Engineers can also use this course to gain Tekla modeling tips, develop a better conception of Tekla modeling tutorials, master Tekla modeling training, and upgrade their career success in the bridge and infrastructure fields.
Conclusion
Revit has become a must-have tool for civil engineers, mainly for modeling retaining walls and other site structures. With the capability of using Revit families for retaining walls, integrating loads in the structures, and collaborating with BIM, engineers can be more accurate and efficient in their designs.
For those eager to learn more, Autodesk Revit Structure tutorials and BIM Revit online courses offer possibilities to learn how to use the software to practice civil engineering and become a more perfect structural designer.
To diversify your knowledge further, we recommend taking a Building Information Modelling (BIM) Course for Civil Engineering and reviewing materials found in Novatr and our resource page, which contain useful tools and information that can benefit those professional individuals who need to move forward in the field.
Was this content helpful to you



.jpg)