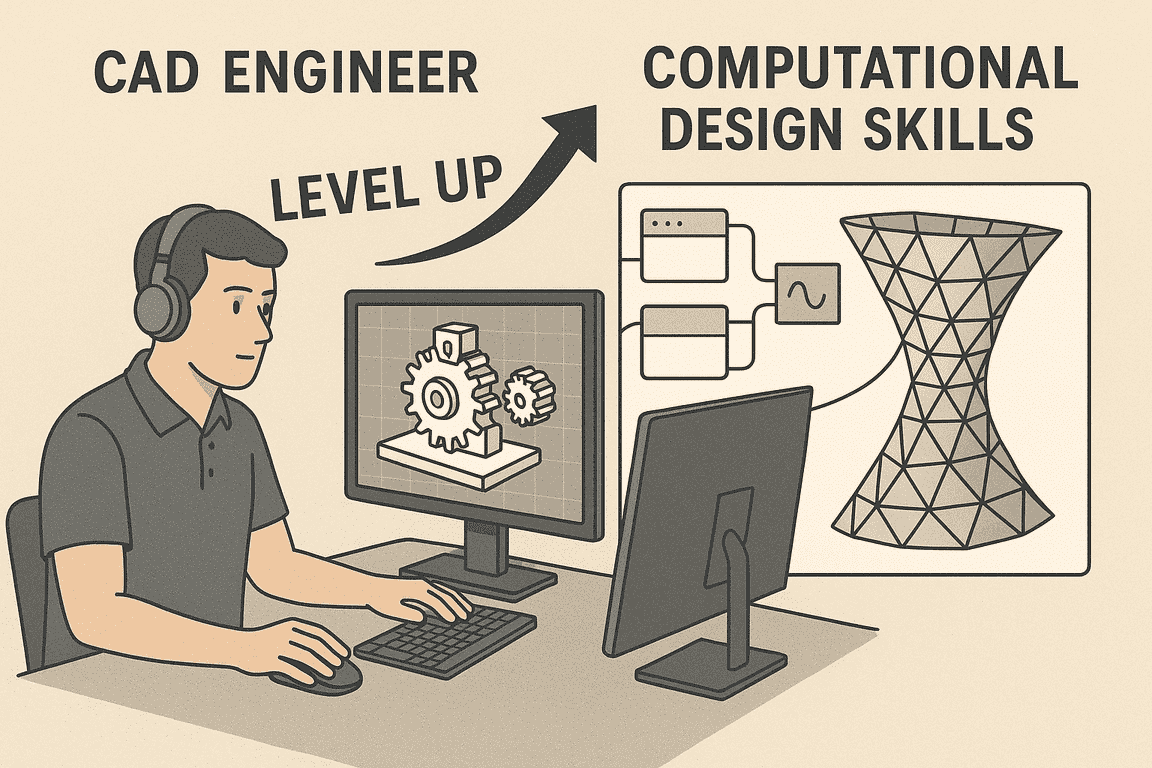
The engineering and construction industry is moving towards a new era of automation, artificial intelligence, and data-dependent decision-making. The existence of the CAD engineer has been over the years, and is essential in delivering both 2D and 3D models using standard and common CAD functions. Nevertheless, the industry will need more by the year 2026.
In the current world, organizations need engineers who can integrate their drafting skills and their CAD engineering computing expertise. Such skills enable the professionals to automate repetitive procedures, achieve simulations, optimize structures, and develop adaptive systems that react to real-world variables.
This shift enables engineers willing to upskill as a CAD engineer to afford what are currently high salaries and new opportunities in generative design, BIM automation, and digital fabrication.
The overall size of the Computer-Aided Engineering (CAE) market is expected to reach USD 11.6 billion by 2026 and USD 14.2 billion by 2027 at a rate of 10.6%. This is evidence of the high uptake of simulation and optimization tools, which are also at the forefront of computation jobs, and therefore, demonstrate that mastering these skills is not optional but essential for staying competitive.
CAD Engineer vs. Computational Engineer
|
Aspect |
CAD Engineer |
Computational Engineer |
|
Approach |
Manual 2D/3D drafting with CAD engineer software |
Algorithm-driven, parametric, and rule-based modelling |
|
Efficiency |
Repetitive edits for every design change |
Automated workflows that adapt instantly |
|
Flexibility |
Static models with limited adaptability |
Dynamic parametric models responding to inputs |
|
Integration |
Drawings and documentation output |
Linked to BIM process automation, fabrication, and simulations |
|
Problem-Solving |
Executes instructions with limited adaptability |
Applies optimisation and generative techniques |
|
Innovation |
Works within fixed tools |
Explores AI, automation, and new workflows |
|
Collaboration |
Supports design teams |
Connects design, engineering, and fabrication |
|
Skillset |
CAD software and drafting |
Coding, parametric tools, BIM automation |
|
Scalability |
Limited by manual edits |
Scales multiple variations quickly |
|
Career Outlook (2026) |
Supportive role in drafting and detailing |
Strategic specialist, high demand across global AEC markets |
|
Value Creation |
Ensures accuracy in drawings |
Delivers performance-driven, cost-efficient designs |
Why CAD Engineers Need to Learn Computation Design?
By 2026, the CAD engineer transitioning into computational workflows will be far better positioned to grow their career, command a higher CAD engineer salary, and take on leadership responsibilities.
The advantages of computational design are wide-ranging. This is why all engineers need to take it up:
1. Automating Repetitive Work with Computational Design Software
Grasshopper 3D and Dynamo scripts also remove the manual CAD work, resulting in increased efficiency in workflows and facilitating BIM process automation.
2. Parametric Flexibility & BIM Automation Tools
Parametric CAD models are rapid because they respond immediately to alterations, in place of redrawing. Dynamo, engineers can create BIM automation applications in documentation, clash detection, and data management.
3. Performance Simulations & Collaboration
Early simulations enhance daylight, energy, or structural optimization. Computer design proficiency among CAD engineers also facilitates multidisciplinary teamwork during automation in BIM.
4. Future-Proof Skillset & Creative Exploration
Understanding Python scripting, Rhino 3D, and Grasshopper 3D allows the engineer to tap into AI-driven design automation and opportunities with complex geometry and facade optimization.
5. Expanded Career Opportunities & Higher CAD Engineer Salary
Upskilling with a computational design course or parametric CAD drafter course opens alternative career paths for CAD engineers in robotics, digital fabrication, and smart cities, often with 20–30% higher salaries.
6. Global Recognition with a Computational Design Certificate
Certification of computational design expertise can enhance your profile's competitiveness and provide you with superior standing in international recruitment pools.
Also Read - How CAD Drafters Can Level with Computational Design?
The Skills CAD Engineers Need to Break Through And What Top Employers Want
CAD engineers must integrate technical expertise and flexibility to address the problems to stand out in 2026. Employers do not just want drafters; they want computational thinkers able to innovate and collaborate in a team.
Software Skills

Employers expect mastery in modern computational design software:
- Learn Rhino 3D – The software to learn about freeform and complex geometry modelling.
- Learn Grasshopper 3D – Rhino parametric plugin, which automates the design process using rules.
- Dynamo – Plays a key role in automating BIM in Revit, to automate documentation and analysis.
- Python Scripting – Supports custom workflows, cross-platform integration, and even more design automation.
Also Read - How CAD Drafters Can Level with Parametric Design?
Soft Skills
In addition to technical competencies, new employers in 2026 put a premium on soft skills to enable non-technological success in a multidisciplinary, cooperative setting:
- Analytical Problem-Solving – Compiling information and reason to yield design solutions.
- Collaboration – Working across multidisciplinary AEC teams.
- Adaptability – Aptitude in fast learning of new computational design software and AI-based tools.
- Creative Thinking – Applying computational methods to explore novel solutions.
In-Demand Specializations
The engineering expertise in areas where employers are looking to hire engineers is:
- Facade Optimization – is a lens to parametrics as a design platform to optimize energy efficiency and aesthetics.
- Structural Rationalization – Inferring simplified and financially feasible systems out of complicated geometries.
- BIM Automation – Designing BIM automation tools eliminate errors and simplify project delivery.
- Digital Fabrication – This is a lead space, including 3D printing, computerized numerical control machining, and modular fabrication.
Employability can be enhanced through specialised training such as a parametric CAD drafter course, a structured computational design course, etc.
Where To Learn These Skills & Get Certified?
Free tutorials are supposed to be taken as a starting point; however, they ordinarily lack depth and hands-on exposure. Computational design is a craft that has to be instructed well, experimented and mentored by a skilled professional to develop technical and artistic problem-solving abilities.
At this point that our Master in Computational Design Course can be utilized through the process of guided learning, industry-focused projects, and mentorship to ensure professionals are career-ready..
Key USP:
- Comprehensive Curriculum: Learn all the professional software used in one program: Rhino, Grasshopper, Dynamo, Python scripting, BIM automation, and generative design.
- Project-Based Learning: Participate in real-world architecture and engineering problems to form a logical professional portfolio.
- Expert Faculty: Professionals with industrial experience in computational design with an experienced industrial career..
- Global Recognition: Earn a computational design certificate that expands work possibilities in your career worldwide.
- Alternative Career Paths: Find your next role beyond CAD drafting into fields in high demand, such as BIM automation engineer and facade optimization consultant, or one field with many possibilities, such as computational design, among others.
- Flexibility: Accessing it online with virtual workshops, instructional videos, and peer communications is possible.
- Career Outcomes: Those who complete computational design courses can obtain positions in major AEC firms and advance more readily through the salary levels of CAD engineers.
If you’re ready to upskill as a CAD engineer, this course offers the most structured path to success.
Conclusion
By 2026, the work of a CAD designer will not simply produce drawings anymore. Learning computational design skills in CAD design enables you to transform the role of a draftsperson to a strategist who influences sustainable, efficient, and innovative projects..
It can be through computational design using repetition (via computational design software to facilitate iterations quickly), BIM automation tools (accelerating delivery), or directing projects with facade optimization. The possibilities are huge. Training to the confidence and credibility levels must be through the right training, like a parametric CAD drafter course or a full-fledged computational design course.
If you’re ready to upskill, explore the Master in Computational Design Course. Visit the Novatr and our resource page for guides, certifications, and tools to help you build your future.
Your drafting skills built the foundation computational design will take your career to the next level.
Was this content helpful to you



.jpg)